AI Hallucinations Explained: What They Are, Why They Happen & How to Avoid Them
What are AI Hallucinations?
An AI hallucination happens when an artificial intelligence system generates information that sounds correct but is not based on real data, verifiable sources, or the content it was given. The key issue is confidence - hallucinations are often delivered as facts, even when they are false.
AI hallucinations happen when AI “fills in the blanks” and makes something up — kind of like seeing shapes in the clouds. It usually happens because the training data isn’t perfect, contains bias, or the model is too complex and makes the wrong assumptions.
Hallucinations vs. Incorrect Data
Hallucinations and incorrect data are related but not the same thing.
Hallucinations occur when the AI invents information that does not exist or is not supported by the input. Incorrect data happens when the AI repeats information from a source that is outdated, incomplete, or wrong.
In simple terms:
- Hallucination: The AI makes it up.
- Incorrect data:
The AI repeats bad input.
Why AI Hallucinates
AI models do not verify truth the way humans do. They predict language based on patterns. When information is missing, unclear, or contradictory, the model may fill in the gaps with something that sounds reasonable. This is why hallucinations are more common when users ask for very specific facts without providing reliable sources.
How to Reduce AI Hallucinations
You can significantly reduce hallucinations by:
- Requiring answers to be based only on provided sources
- Asking the AI to cite or quote its sources
- Allowing the AI to say 'not found' or 'unknown'
- Using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with trusted documents
- Adding a verification or fact-checking step
Example of Real-Life Hallucination:
I gave Chat GPT this prompt:
Can you recommend a great paint party experience in Cambridge, MA?
And it gave me the following company name and pictures.

I responded: Funny, you displayed pictures from a different company. They belong to Canvas n Cup. Then I got this reply:
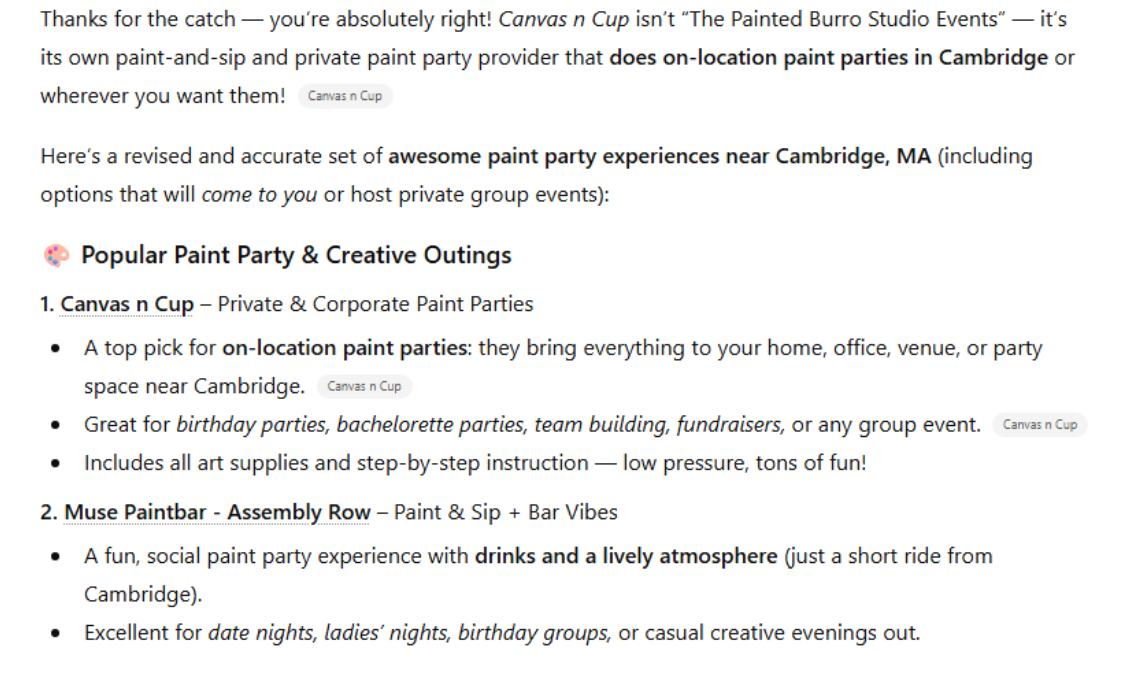
Hallucination one: The Painted Burrow is a Bar
Hallucination two: The images belong to two different businesses, one being Canvas-n-Cup.
How often is AI wrong?
Hallucination rates for common AI models.
There is no single universal hallucination rate because it depends on the task (summarization vs. Q&A vs. coding), the prompt, and whether sources are provided. ChatGPT and Claude have the highest hallucination rates as summarized below.
| Model (as listed on leaderboard) | Hallucination rate (summarization) |
|---|---|
| google/gemini-2.5-flash-lite | 3.3% |
| meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct-Turbo | 4.1% |
| mistralai/mistral-large-2411 | 4.5% |
| mistralai/mistral-small-2501 | 5.1% |
| openai/gpt-4.1-2025-04-14 | 5.6% |
| xai-org/grok-3 | 5.8% |
| deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3 | 6.1% |
| google/gemini-2.5-pro | 7.0% |
| google/gemini-2.5-flash | 7.8% |
| openai/gpt-4o-2024-08-06 | 9.6% |
| anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-20250514 | 10.3% |
| anthropic/claude-opus-4-20250514 | 12.0% |
Source: Vectara Hallucination Leaderboard (updated January 5, 2026), summarization faithfulness measured with their HHEM evaluator and a curated document set.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are AI hallucinations the same as AI errors?
Not always. Hallucinations are a specific type of error where the AI invents information. Other errors may come from incorrect or outdated data sources.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
RAG is when an AI “looks up the answer” before it answers you.
Instead of the AI only using what it already knows (from training), it does this:
Retrieval = it searches a set of trusted information
(like your website pages, PDFs, FAQs, knowledge base, Google Drive docs, etc.)
Augmented = it brings the most relevant pieces into context
Generation = then it writes the response using that info
Does using RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) eliminate hallucinations?
No. RAG reduces hallucinations by grounding answers in documents, but AI can still misinterpret or overgeneralize the source material.
Are some AI models better than others at avoiding hallucinations?
Yes. Newer and larger models generally hallucinate less, especially when given clear instructions and trusted source material.
Why do hallucinations matter for businesses?
Hallucinations can lead to incorrect marketing claims, legal risks, poor customer trust, and bad decision-making if not caught.